Imagine yourself having a fresh cup of coffee in global coffeehouse. Have you ever paused to think for a second about the forces that helped bring coffee to your table, such as government policies, international trends, and the impact of technologies? Climatic changes, such as drought, may increase the price of coffee beans. A newly imposed import duty could, in turn, have pushed the cafe’s supplier prices high. And new labour laws might have affected how those beans were harvested, packed, and shipped.
This is the invisible world in which businesses operate every day, and that’s exactly where PESTLE analysis comes in. This framework will help you predict the changes happening around the globe and help you minimise or eliminate the losses that might occur. It’s not just for big corporations, either. Whether you’re running a side hustle or thinking about launching a startup, knowing what’s happening outside your business is just as important as what’s happening inside.
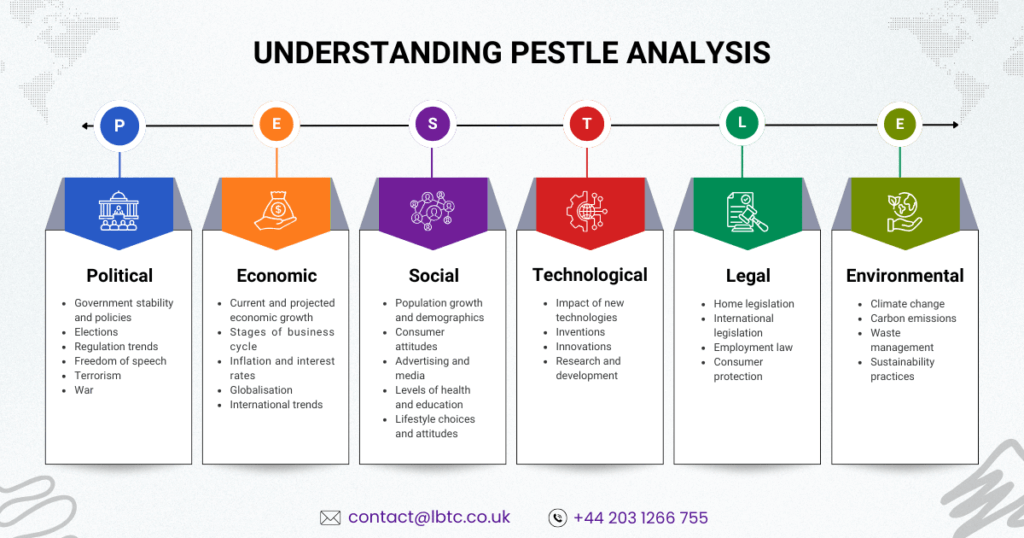
What is PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE (sometimes spelled as PESTEL) stands for:
P – Political
E – Economic
S – Social
T – Technological
L – Legal
E – Environmental
Each part of the PESTLE framework helps you understand the external forces that could affect your business. It helps you most when you’re planning to launch a new product, conducting market research, or simply staying ahead of potential risks.
1. Political factors
These refer to how industries and businesses are influenced and affected by changes in government policies. A sudden shift in government might bring changes to labour laws and taxes, which could affect business operations. A change in the trade agreements can completely reshape supply chains.
Brexit, for example, created uncertainty for companies operating between the UK and EU, impacting the supply chains, tariffs, and labour mobility.
Government stability and policies, Elections, Regulatory trends, Freedom of speech, Terrorism, and War are factors to be considered.
2. Economic Factors
Customer behaviour and business performance depend upon economic indicators such as inflation, interest rates, exchange rates, and economic growth rates.
Currency fluctuations can also be a concern for companies that import and export the goods. When the domestic unit depreciates, the price of imported inputs escalates, frequently compressing profit margins and forcing managers to reassess pricing or sourcing decisions.
Current and Projected Economic growth, Stages of the Business Cycle, Inflation and interest rates, Globalisation, and international trends are to be considered as factors.
3. Social Factors
Social factors examine the cultural and demographic aspects of the external environment.
The rise of health consciousness has significantly influenced the food and beverage industry, prompting companies to produce alternatives such as organic and low-sugar products. They also changed the packaging of bottles to facilitate recycling and help save the environment.
The factors to be considered are Population growth and demographics, consumer attitudes, Advertising and media, Levels of health and education, Lifestyle choices and attitudes.
4. Technological Factors
Technology evolves fast. For businesses, this means staying updated on innovations that could disrupt their industry.
Consider how streaming services like Netflix have disrupted traditional television and video rental stores.
The factors to be considered are the impact of new technologies, inventions, innovations, Research and Development.
5. Legal Factors
Laws and regulations can both create opportunities and pose obstacles. A business that fails to comply with new data protection regulations, for instance, could face hefty fines and reputational damage. On the brighter side, new favourable legislation can offer growth opportunities.
The introduction of GDPR in Europe forced companies worldwide to rethink how they handle user data.
The factors to be considered are home legislation, international legislation, employment law, and consumer protection.
6. Environmental Factors
Today, businesses can no longer afford to ignore environmental considerations.
Many consumers now prefer eco-friendly brands, and governments are imposing stricter regulations on emissions and waste. Companies that integrate environmental responsibility into their operations often find themselves gaining favour with customers and regulators alike.
Factors such as climate change, carbon emissions, waste management, and sustainability practices have become central to corporate strategy.
Why Use PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE isn’t about predicting the future—it’s about preparing for it. By identifying external threats and opportunities, businesses can:
- Make more informed strategic decisions
- Mitigate risks before they arise
- Spot new opportunities in the market
- Align their goals with external realities
That’s why frameworks like PESTLE are commonly taught in leadership training courses—because they empower leaders to think beyond the immediate and plan for what’s coming next.
Conclusion:
PESTLE analysis helps you see the bigger picture and stay ahead of change. It’s not just a tool for big companies—it’s essential for anyone making smart, forward-thinking decisions. That’s why it’s a key part of many leadership training courses today—because great leaders don’t just react; they prepare.

Leave a Reply